A new approach for approximating conservation laws has been tested: instead of monitoring the changes of the means of a quantity within a certain volume over time like a finite volume procedure, this method mimics the behavior of simple solutions.
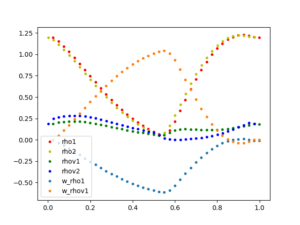
First the current state is split into waves w, each aligned along one of the eigenvectors of the Fluxjacobian and living on its own grid. Then the corresponding grids are being moved with their eigenvelocity and finally all waves w are being overlayed and normalized yielding the solution after one timestep.
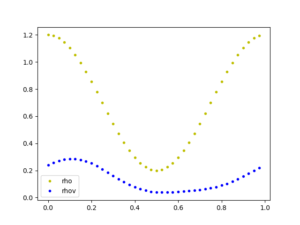
The plots show the solution of isothermal Euler equations at Time T=0.0000 (initial condition) and T=0.0025 with N=40 gridpoints for each mesh.